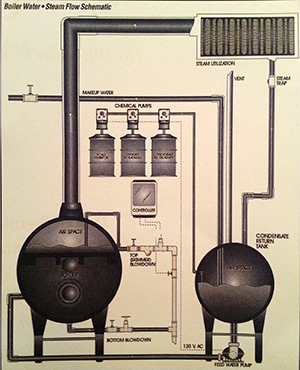
Total Water Management

Industrial plants, institutional facilities, and commercial applications all agree that water is a vital part of their operations. Both manufacturing processes and control of the environment depend heavily on proper water treatment. Boilers, cooling towers, water plants and their associated equipment are the life blood of their operation and require Total Water Management to assure long life, as well as safe and efficient operation.
Water Problems
All water sources contain impurities and present different problems for plant equipment. Scale, corrosion, and fouling are some of the problems associated with improper water treatment. Unaddressed, these problems will cause loss in energy efficiency, reduced system capacity, equipment failure and possible plant/facility shut-down. The economic impact can have major consequences!
Solutions
Delta Chemical Corporation works with plant personal to form problem solving teams. Solutions are formulated through detailed analytical services and costume product development. Close interaction with key plant personal allows for proper implementation of the solution. Operator training and personal service ensure continued success. Total Water management is required to protect expensive operating/process equipment and prevent costly cleaning, failures, and down time.
Economic Impact
Total Water Management is a complete approach to insure maximum return on your water treatment program investment. Program results and performance are achieved through properly applied chemical programs that utilize most advanced products in the industry. Water conservation, water re-use, and reduced energy costs are some of the savings that can actually pay for the cost of the water treatment program.
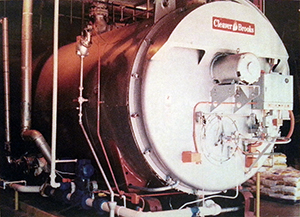
Boiler Water Problems
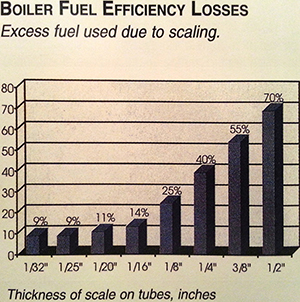
Scaling
As water is heated and converted into steam, contaminants brought into a boiler with makeup water are left behind, the boiler functions as a distillation unit, taking pure water out as steam, and leaving behind concentrated minerals, and other contaminants in the boiler. Scale forms as a result of the precipitation of normally soluble solids that become insoluble as temperature increases. Some examples of boiling scale are calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate, and calcium silicate.
Corrosion
Corrosion is a general term that indicates the conversion of a metal into a soluble compound. In the case of boiler metal, corrosion is the conversion of steel into rust. In a boiler two types of corrosion are prevalent: 1) Oxygen pitting corrosion seen on the tubes and in the preboiler section. 2) Low pH corrosion, seen in the condensate return system. Corrosion of either type can lead to failure of critical parts of the boiler system, deposition of corrosion products in critical heat exchange areas, and overall efficiency loss.
Carryover
Carryover is caused by either priming or foaming. Priming is the sudden violent eruption of boiler water which is carried along with steam out the boiler, usually caused by mechanical conditions. Priming can cause deposits in and around the main steam header valve in a short period of time. Foaming causes carryover by forming a stable froth on the boiler water, which is then carried out with the steam. Over a period of time, deposits due to foaming can completely plug a steam or condensate line.
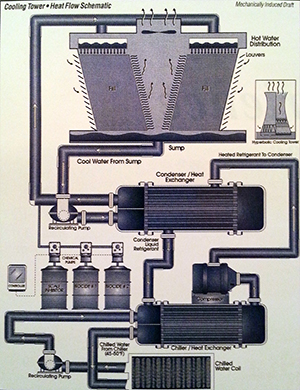
Cooling Water Problems
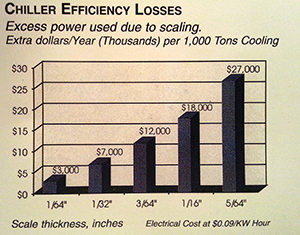
Scaling
Water formed deposits result from naturally occurring minerals precipitating from the water to form scale. The most common scale formations are calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate and silica or silicate. Scale buildup on surfaces can be extremely hard and difficult to remove. Scaling will drastically reduce heat transfer capacity and system energy efficiency.
Corrosion
Cooling systems are exposed to many types of corrosion from general electrochemical corrosion, to pitting caused by deposit, electrolysis, or micro-organisms. Corrosion can reduce the life-span of equipment by years, requiring expensive replacement. It can lead to costly equipment repairs and product downtime. Corrosion related deposits leads to reduced capacity and waste energy because of heat transfer efficiency losses.
Fouling
Fouling occurs when solid materials form or contribute to the formation of deposits on equipment surfaces. they are introduced to the systems as suspended solids and many enter by the makeup of the water, from corrosion by-products, or as airborne materials. Examples include mud, sand, salt, clay, oils, debris, organics, microbes, etc. These materials adhere to heat transfer surfaces and reduce heat transfer and water flow.
Microbiological Contamination
Microbiological problems associated with industrial cooling water systems era caused by algae, fungi, and bacteria. They cause plugging, fouling, corrosion, and destruction of wooden cooling tower components. Many different bacteria species may exist in cooling water systems. Some of the problems caused include severe bacterial slimes and fouling, sulfuric acid, under-deposit corrosion and health hazards.


